1c server error establishing connection. Installing the 1C:Enterprise server
Question: Com Error in Processing Filling
Hello.
8.2 Retail 1.
I connect to 8.1 Not a typical conf.
I connect via com to the database and try to create a document, but when calling “CreateDocument()” or “GetObject()” an error occurs in the procedure ProcessingFilling. see fig.
I try the same thing in the 8.1 database itself, but there is no error, and I also don’t enter Filling Processing.
What could be wrong?
Answer: turboq, a crookedly written document module!
Added after 5 minutes
She is not called! She's trying to compile! But since when connecting via ComConnector the Dialog Mode issue does NOT EXIST, the document module cannot be compiled.
For such cases, when it is necessary to implement work with a dialog in an object module, use instructions to the preprocessor
This is not your mistake, but an error in the document module in the database you are connecting to.
In the database, the code is executed on the client and there is a Dialogue Mode, so everything happens without errors
Do not use ComConnector, V8.Application for connection, then interface things will be available to you
Added after 5 minutes
=======================================================================================================================
from the description of the external connection (SP) I highlighted in bold what you should read about ComConnections
Description:
In general, working with 1C:Enterprise 8 via an external connection is similar to working with 1C:Enterprise in server Automation mode. The main differences are as follows:
- In the case of an Automation server, a full-fledged 1C:Enterprise 8 application is launched, and in the case of an external connection, a relatively small in-process COM server is launched.
- When working through an external connection, functionality that is in one way or another related to the organization of the 1C:Enterprise 8 user interface is not available;
- When working with an external connection, the managed application module (regular application module) of the 1C:Enterprise 8 configuration is not used. Its role when working with an external connection is played by the external connection module.
- Faster connection establishment, since there is no need to create a separate operating system process, and all actions are performed within the calling process;
- Faster access to the properties and methods of 1C:Enterprise objects, since organizing an access does not require interprocess communication;
- Less consumption of operating system resources.
- a COM connection manager is created, with the help of which the connection is established;
- a call is made to the Connect method of the COM connection manager. The Connect method returns an external connection to the 1C:Enterprise 8 infobase;
- through an external connection, access to valid methods, properties and objects of the infobase with which the connection is established is made.
An outer join provides full access to its global context. Therefore, an external connection as its methods can have: system constants, values of objects specified in the configurator, access to which is carried out using managers (for example, constants, enumerations, directories, documents, document logs, reports, processing, plans of characteristics types, charts of accounts , calculation type plans, registers), as well as variables declared in the external connection module with the Export keyword.
Availability:
The combination of 1C:Enterprise server and PostgreSQL is the second most popular among 1C installations and the most used solution on the Linux platform. Unlike implementations based on Windows and MSSQL, where it is difficult to make it not work, implementations based on Linux are fraught with many pitfalls for an inexperienced administrator. It often happens that everything seems to be done correctly, but error follows error. Today we will look at the most typical of them.
general information
Before you start looking for installation errors and, in general, start implementing the server version of 1C:Enterprise, it would be nice to refresh your understanding of how it works:
In small implementations, the 1C server and the DBMS server are usually combined on one physical server, which slightly narrows the range of possible errors. In our case, we will consider a situation where the servers are located on different machines. In our test lab we deployed the following scheme:
 We have two servers running Ubuntu 12.04 x64, one of them has the 1C:Enterprise server version 8.3 installed, the other has PostgreSQL 9.04 from Ethersoft, as well as a client running Windows. We remind you that the client is working only with the 1C server, which, in turn, generates the necessary requests to the DBMS server. No requests from client to database management server not happening.
We have two servers running Ubuntu 12.04 x64, one of them has the 1C:Enterprise server version 8.3 installed, the other has PostgreSQL 9.04 from Ethersoft, as well as a client running Windows. We remind you that the client is working only with the 1C server, which, in turn, generates the necessary requests to the DBMS server. No requests from client to database management server not happening.
IMPORTANT: user "postgres" is not authenticated (Ident)

This error occurs when servers are distributed across different PCs due to incorrectly configured authentication on the local network. To resolve, open /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf, find the line:
Host all all 192.168.31.0/24 ident
and bring it to this form:
Host all all 192.168.31.0/24 md5
Where 192.168.31.0/24 - the range of your local network. If there is no such line, it should be created in the section IPv4 local connections.
Database server not found
could not translate host name "NAME" to address: Temporary failure in name resolution
 At first glance, the error is clear: the client cannot resolve the name of the DBMS server, a typical error for small networks where there is no local DNS server. The solution is to add an entry to the file hosts on the client, which does not give any result...
At first glance, the error is clear: the client cannot resolve the name of the DBMS server, a typical error for small networks where there is no local DNS server. The solution is to add an entry to the file hosts on the client, which does not give any result...
And now let’s remember what was said a little earlier. The client of the DBMS server is the 1C server, but not the client PC, therefore the entry must be added to the file on the 1C:Enterprise server /etc/hosts on the Linux platform or on the Windows platform.

A similar error will occur if you forgot to add record type A for the DBMS server on the local DNS server.
Error when performing an operation with the infobase
server_addr=NAME descr=11001(0x00002AF9): This host is unknown.
 Like the previous one, this error is due to the client incorrectly resolving the server name. This time it is the client PC. As a solution, add to the file /etc/hosts on Linux platform or C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts on the Windows platform, an entry like this:
Like the previous one, this error is due to the client incorrectly resolving the server name. This time it is the client PC. As a solution, add to the file /etc/hosts on Linux platform or C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts on the Windows platform, an entry like this:
192.168.31.83SRV-1C-1204
where you indicate the address and name of your 1C:Enterprise server. If using local DNS, you should add A-record for 1C server.
DBMS error: DATABASE is not usable
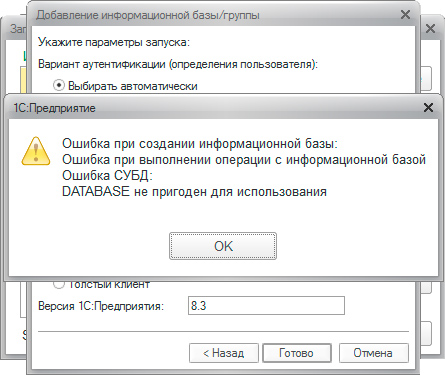 A much more serious error, which indicates that you installed a version of PostgreSQL that is incompatible with 1C:Enterprise or made serious mistakes during installation, for example, did not install all the necessary dependencies, in particular the library libICU.
A much more serious error, which indicates that you installed a version of PostgreSQL that is incompatible with 1C:Enterprise or made serious mistakes during installation, for example, did not install all the necessary dependencies, in particular the library libICU.
If you have sufficient experience in administering Linux systems, you can try to install the necessary libraries and reinitialize the DBMS cluster. Otherwise, it is better to reinstall PostgreSQL, remembering to delete the contents of the folder /var/lib/pgsql.
This error can also occur when using assemblies 9.1.x And 9.2.x Postgre@Etersoft, see details below.
DBMS error:
ERROR: could not load library "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/postgresql/fasttrun.so"
 Quite a specific error, typical for assemblies 9.1.x And 9.2.x Postgre@Etersoft, can also lead to the previous error. The reason lies in an uncorrected bug in the fasttrun.so library. The solution is to roll back to the build 9.0.x Postgre@Etersoft.
Quite a specific error, typical for assemblies 9.1.x And 9.2.x Postgre@Etersoft, can also lead to the previous error. The reason lies in an uncorrected bug in the fasttrun.so library. The solution is to roll back to the build 9.0.x Postgre@Etersoft.
DBMS error
ERROR: type "mvarchar" does not exist at character 31
 Occurs if the database was created without the help of the 1C:Enterprise system. Remember, to work with 1C, databases should be created only using the tools of the 1C platform: through the console
Occurs if the database was created without the help of the 1C:Enterprise system. Remember, to work with 1C, databases should be created only using the tools of the 1C platform: through the console

or through the 1C launcher.

Database server not found
IMPORTANT: user "postgres" is not authenticated (by password)
 A very simple mistake. The password for the postgres DBMS superuser is specified incorrectly. There are two solutions: remember your password or change it. In the second case, you will need to change the password in the properties of all existing infobases through the snap-in Administration of 1C Enterprise servers.
A very simple mistake. The password for the postgres DBMS superuser is specified incorrectly. There are two solutions: remember your password or change it. In the second case, you will need to change the password in the properties of all existing infobases through the snap-in Administration of 1C Enterprise servers.
Database server not found
FATAL: database "NAME" does not exist
 Another very simple mistake. Its meaning boils down to the fact that the specified database does not exist. Most often it occurs due to an error in specifying the database name. It should be remembered that the 1C information base in the cluster and the DBMS database are two different entities and may have different names. You should also remember that Linux systems are case sensitive and for them unf83 And UNF83 two different names.
Another very simple mistake. Its meaning boils down to the fact that the specified database does not exist. Most often it occurs due to an error in specifying the database name. It should be remembered that the 1C information base in the cluster and the DBMS database are two different entities and may have different names. You should also remember that Linux systems are case sensitive and for them unf83 And UNF83 two different names.
Tags:
- Dr. Cuddy: We need a diagnosis. Woman, 26 years old, gas explosion under the building, she was pulled out of the rubble after 6 hours. Two surgeries due to numerous fractures and burns...
Dr. House: I think the broken bones are the result of a building collapsing on her head. - Dr. House: Imagine that the roof of the storage room collapsed on your favorite scrubber. And it starts to overheat.
Cleaner: Why should I love a floor scrubber? Okay... Maybe the impact damaged something in the electrical wiring. Or something flowed inside and ruined it...
Dr. House: HM interesting. Penetration of infection through lacerations. The bacteria would react to antibiotics. The heat is too intense for a virus. Possibly parasites or fungi.
Cleaner:Or lupus.
House turns around in amazement.
Cleaner: My grandmother has lupus.
Dr. House:(puzzled) Okay, auto-immune. I'll check for lupus. Although an infection is more likely. It would be nice to have her map too. Let's get to the worst part of the job. To communicate with the family of the floor scrubber.
- Dr. House: The card says she was sick before the building collapsed.
Patient's husband: I think it's a common cold. What, do you think this is connected?
Dr. House: Her illness with her illness? Sometimes it happens. - Patient's mother: Does the diary say that my daughter is taking these pills?
Dr. House: No, but from a medical point of view...
Dr. Cuddy: Did you find the pills in her house?
Dr. House: Apparently she hid them in her purse. I thought it would be indecent to search under 1000 tons of debris. - Surgeon: She's bleeding everywhere, unless the abortion was done with a shotgun.
This article shows an example of general principles for analyzing technological issues that may arise when working with 1C:Enterprise 8.1.
Everyone loves to give advice, but when it comes down to it, everyone suddenly has more important things to do :))). It would probably be fair to immediately warn that this material was written by me more as information for thought, and not as a theory for solving personal problems and unpleasant situations at work. Nevertheless, I think that the examples given here from my practice can be useful when analyzing similar problems.
The following will be discussed as examples:
Example 1. A user complained about the impossibility of launching 1C: Accounting.
Message text:
"Error connecting to server 1c: Enterprise 8.1:
server_addr=App1С:1540=Error in network access to server
(Windows sockets - 10061(0x0000274D)
No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it) line =567
Example 2. Access to the information base is “lost.”
Message text:
Error when performing an operation with the infobase
Microsoft OLE DB provider for SQL Server: Login failed for user 'user1c'
H RESULT=80040E4D, SQLSrvr: Error state=1, Severity=E, native=18456, line=1
Example 3. Strange "unknown" error.
Text of the message: “An unknown error occurred on the 1C Enterprise server (80010108)”
1. Determination of the text (manifestation) of the error and localization of the source of occurrence

- Record the error (text and/or other information that may be useful for analyzing the problem). It is better to record the problem using a technology log. Conclusion: if you do not use the technological log for other tasks, configure it to constantly collect “exception” events (EXCP) and generate dumps in case of a platform crash.
- Record the time the error occurred. This will further help localize the location of the study of various logs.
- READ the text of the message, try to immediately understand the source of the problem from the contents of this text.
- Search for a solution in the text of the message on the Internet or in other sources known to you for solving the problem.
- Those who have not previously dealt with problems with platform errors will not solve them, look for those who have done or are doing this.
Note. Example 1. A search below in the section “Where can I find a ready-made solution” using the text “10061” given on this page will immediately show an explanation of the reason and solution: The service has stopped on the application server" 1c server agent:Enterprise 8.1". Accordingly, it must be launched, for example from the command line:
net start Server Agent 1C:Enterprise 8.1
If the application server does not start, in some cases make a copy of the C:\Program Files\1cv81\server folder and delete the contents before attempting to start.
When connecting to the 1C server from the console we get:
Server error or connection terminated by administrator
Stream format error
When starting the SQL database we get the error:
There was a server error or the connection was terminated by the administrator.
Stream format error
And so, the initial data:
Freshly installed Windows 7 Professional x64, all updates, etc. (the problem occurs on both Server 2008 and 2008R2)
1C x64 server installed (tried 32bit too)
Everything works until reboot. After a reboot, when trying to connect to a database in SQL or opening a cluster in the 1C console, we get a response with the following pictures:
When connecting to the 1C server from the console we get:
Error connecting to 1C:Enterprise 8.2 server:
Server error or connection terminated by administrator
Stream format error
When starting the SQL database we get the error:
An error occurred while performing an operation with the infobase.
There was a server error or the connection was terminated by the administrator.
Stream format error

To be able to launch the database and connect to the cluster from the console, the only thing that helped was:
1. Stop the server service 1C:Enterprise 8.2
2. Removing processes rmngr.exe rphost.exe (it crashes when rmngr.exe ends).
3. Cleaning the directory C:\Program Files\1cv82\srvinfo\reg_1541\snccntx (for a 32-bit server C:\Program Files (x86)\1cv82\srvinfo\reg_1541\snccntx)
4. Starting the 1C:Enterprise 8.2 server service
However, while working with the SQL configuration, it was possible to unexpectedly catch an emergency shutdown of 1SKi and then receive the same errors.
Were tested:
1. different releases, different servers,
2. various users: System, Administrator, USR1CV82.
3. forced assignment of full rights to these directories for these users C:\Program Files\1cv82\ (for a 32-bit server C:\Program Files (x86)\1cv82\) with inheritance to child objects.
4. dozens of reboots and much more.
However, the reason turned out to be much more unexpected!
Dereferencing in Windows 7 (Server 2008, 2008R2, probably 2012)
Try pinging your computer by name. What you see will determine the possibility of using my solution.
It's easy to do:
1. Launch the command line (Win+R, type cmd and click OK)
2. At the command line, type the command "Ping" followed by a space and the name of your computer. It is the name, not its IP address. Press Enter.
3. If the system starts pinging itself through an address like fabc:de12:3456:7890:ABCD:EF98:7654:3210, or another IP address different from yours
Welcome to the private club of Windows 7 dereference bug features.
The basis of the problem lies in the fact that the 1C server cannot identify itself by name.
But displaying your IP as IPv6 is one of the most common reasons for this error.
Another reason may be a periodic connection to another network (let’s say a VPN) when a new interface is created and Windows again begins to dereference itself “incorrectly”.
Below I will describe two solutions to bypass this “feature”.
First I want to warn you:
You perform all actions with your computer at your own peril and risk.
Option #1 Add your PC and its IP to Hosts
1. You need to find the hosts file in the folder C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc If you don’t see the Hosts file in this folder, then it is simply hidden. Then You can press the ALT key and, in the menu that appears, select “Tools” - “Folder Options” - “View” and take off There is a checkbox for "Hide protected system files". You can also set the switch “Show hidden files, folders, drives”, then everything will be visible.(After manipulating Hosts, I recommend returning the checkbox to its original place, so as not to accidentally catch anything in the future)
2. Open this file in Notepad (notepad) and add a line like 192.168.0.1 Server (IP address PC Name) to the end. Save and close the file.
3. Try to ping your PC again using the name. If you again don’t see the required IP, something went wrong... Perhaps the antivirus returned an old version of the file (Casper likes this) or something else.
In general, you need to achieve the correct address when pinging through a name.

Trying to be ahead of the curve, Windows 7 not only installs IPv6 on all interfaces at once, it also sets it as the default when dereferencing. However, today few people use this protocol, and therefore it can/should be disabled. Remember that unchecking the IPv6 protocol in the network card interface will do nothing!
- Click Win+R, type regedit and press Enter. The Registry Editor will open.
- If you are prompted to allow actions, click in the dialog box User Account Control button Continue.
- Locate and select the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters\
- Double-click the item DisabledComponents to change a parameter DisabledComponents.
If the parameter DisabledComponents is missing, it must be created. For this:- While on a branch Parameters on the menu Edit select item Create, and then - DWORD value (32 bits).
- Type DisabledComponents and press Enter.
I would like to remind you that both solutions are not a panacea, and do not actually allow you to bypass the error, but not eliminate its cause
In addition to the file version, the 1C:Enterprise system can work with information bases in a client-server version. In the latter case, an architecture is understood that consists of several software layers, schematically depicted in the figure below.
- Client applications, thin clients and web clients- this is “1C:Enterprise” in various launch modes with which the end user works. For client applications and thin clients, a web browser is sufficient on users' computers (or on), for a web client.
- Server cluster "1C:Enterprise" is a collection of work processes running on one or more computers and a list of information bases that are located in this cluster. In the server cluster, all the work of application objects is performed, preparations are made for displaying forms (reading infobase objects, filling out form data, arranging elements, etc.) and the command interface, generating reports, and running background jobs. Clients only display information prepared in the server cluster. In addition, service files are stored on the 1C:Enterprise cluster server, as well as an infobase registration log.
- Database server— on the database server, direct storage and work with data takes place, provided by one of the following database management systems (DBMS) supported by the 1C:Enterprise system:
- Microsoft SQL Server from Microsoft SQL Server 2000 and higher;
- PostgrageSQL since version 8.1;
- IBM DB2 since version 9.1;
- Oracle Database since version 10g Release 2.
- Web server required only for web clients and one of the thin client options. Provides interaction of these types of connections with a cluster of 1C:Enterprise servers.
It is also worth noting that each software layer does not necessarily have to be located on a separate physical computer. A server cluster can be located on the same computer with a database server, web server, etc. For example, the following work structure is often found in small organizations:

In this article I will describe the installation of the 1C:Enterprise server version 8.3.4.389 (for other versions of the 1C:Enterprise platform 8.1, 8.2 and 8.3 the steps are similar) on one computer running Windows Server 2008 (R2) or Windows Server 2012 (R2). Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (R2) or Microsoft SQL Server 2012 will be considered as a DBMS. For this we will need:
- A computer that meets the system requirements for installing the 1C:Enterprise server and with the OS installed on this computer or .
- A computer for a database server, also running an OS or (can be the computer from step 1).
- Local administrator rights on both computers.
- Distribution kit for installing the 1C:Enterprise server 8.
- Software license or HASP4 Net protection key for the 1C:Enterprise server.
- Distribution kit for installing Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (R2) or Microsoft SQL Server 2012.
2. Installation of MS SQL Server DBMS
We install the MS SQL Server DBMS on the computer that serves as the database server. To operate the 1C:Enterprise system, it is enough to install the following components:
- Database Engine Services
- Management Tools - Basic
- Management Tools - Complete.
Select sorting options " Cyrillic_General_CI_AS" Details about installing systems
3. Configuring Windows Firewall for DBMS operation
If the database server and the 1C:Enterprise cluster server are located on different physical computers, you need to configure the Windows Firewall on the database server so that the 1C:Enterprise server can work with the DBMS, namely, open incoming connections on the port 1433 (for default SQL Server instance).
- I wrote in detail about setting up Windows Firewall for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (R2) / 2012.
4. Adding a user to MS SQL Server
Next, we will add a separate user to MS SQL Server, under which the 1C:Enterprise server databases will be connected. This user will also be the owner of these databases. The user to be added must be authorized on the server using a password and have the following set of roles: dbcreator, processadmin, public. Details about adding a user to
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (R2) I wrote.
- I wrote Microsoft SQL Server 2012.
5. Installation of the 1C:Enterprise server
Now let's move on to installing the 1C:Enterprise server files and starting the corresponding service. Installation requires a distribution kit of the 1C:Enterprise technology platform. From the list of supplied distributions, the following are suitable:
- 1C:Enterprise technology platform for Windows - allows installation of a 32-bit 1C:Enterprise server
- 1C:Enterprise server (64-bit) for Windows - allows installation of both 32-bit and 64-bit 1C:Enterprise servers
(There is also an extended version of KORP server 1C:Enterprise 8.3, details can be found on the 1C website)
Open the directory with the 1C:Enterprise server installation files and run the file setup.exe.

The 1C:Enterprise system installation assistant will start. On the first page click " Further».

On the next page you need to select the components that will be installed; we require the following components:
- Server 1C:Enterprise— 1C:Enterprise server components
- Server administration 1C:Enterprise 8— additional components for administering a cluster of 1C:Enterprise servers
The remaining components (the list of components may depend on the specific distribution), depending on the need, can also be installed on this computer. Having made your choice, click “ Further».

Select the interface language that will be used by default and click " Further».

If the 1C:Enterprise server is installed as a Windows service (and in most cases it should be installed as such), I recommend immediately creating a separate user under which the created service will be launched. For this
- Leave the flag "on" Install 1C:Enterprise server as a Windows service (recommended)»;
- We move the corresponding switch to “ Create user USR1CV8».
- Enter the password for the user being created twice. By default, the password must comply with the Windows password policy. You can read more about this:
- For Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (R2) - ;
- For Microsoft Windows Server 2012 - .
You can also select an existing user to run the 1C:Enterprise server. In this case, the selected user must have the following rights:
- Log on as a service
- Log on as a batch job
- Performance Log Users.
Also, the user must be given the necessary rights to the directory of server service files (by default C:\Program Files\1cv8\srvinfo for 64-bit and C:\Program Files (x86)\1cv8\srvinfo for a 32-bit server).
Automatically created user USR1CV8 will have all of the above rights.
After filling in the appropriate parameters, click “ Further».

And finally, click “ Install» to start the installation. This will copy the files of the selected components, create configuration files, register program components, create shortcuts, and also start the 1C:Enterprise server service.

Once the installation is complete, the assistant will prompt you to install the protection driver - HASP Device Driver. If you are using a software license for the 1C:Enterprise server, there is no need to install the driver. Leave or remove the flag " Install protection driver" and click " Further».


